Ceramic products have long been valued for their durability and aesthetic appeal, but ensuring their safety is crucial, particularly for importers. Ceramic product safety standards protect consumers and businesses from health risks and legal complications. This article explores key safety standards for ceramic products and how importers can navigate them effectively.
What Are Ceramic Product Safety Standards?
Ceramic product safety standards are a set of regulations and guidelines designed to ensure that ceramic items are safe for their intended use. These standards are essential for protecting public health, maintaining product quality, and ensuring compliance with legal requirements.
Key aspects of ceramic product safety standards include:
- Food-grade Safety: Ensuring that ceramic items used for food or beverages do not leach harmful substances into what they contain. This is particularly critical for tableware such as plates, bowls, and mugs.
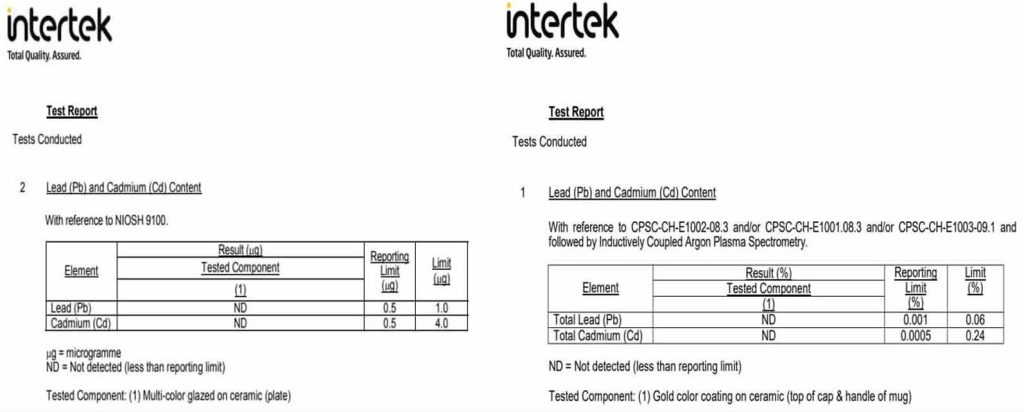
- Lead and Cadmium Limits: Glazes and decorations on ceramics can sometimes contain these toxic heavy metals. Safety standards set strict limits on the permissible levels to prevent health risks.The following are the test results previously conducted by HomeyCeramic, demonstrating that our products meet the testing standards.
- Thermal Shock Resistance: Testing ensures that ceramic products can withstand sudden temperature changes without cracking or breaking. This is vital for bakeware and other heat-exposed items.
- Chemical Safety: Ensuring that no harmful chemicals are present in the ceramic material or applied finishes. This includes compliance with broader chemical regulations, such as REACH in the European Union.
These standards vary globally, reflecting different regulatory priorities and market demands:
- In the European Union (EU), stringent limits on lead and cadmium are enforced under the Food Contact Materials Regulation.
- In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) sets rules for ceramic items in contact with food.
- Australia and other countries have similar regulations tailored to their domestic needs.
By adhering to these safety standards, ceramic products gain credibility and ensure customer trust, making compliance a critical factor for importers and manufacturers.
Key Standards and Certifications to Know
- FDA Compliance (USA): Ensures ceramic tableware is safe for food and beverage use by testing for harmful substances.
- LFGB Standard (Germany): Regulates materials that come into contact with food, focusing on non-toxic and safe components.
- REACH Regulations (EU): Aims to protect consumers by controlling chemical usage in products.
- ISO Standards: Internationally recognised benchmarks for quality and safety in ceramic production.
Safety Considerations for Different Ceramic Products
Different types of ceramic products are subject to varying safety requirements based on their intended use. Below are specific considerations:
- Tableware: Plates, mugs, and bowls must meet stringent food-contact safety regulations to prevent harmful substances from leaching into food and drinks. Glazes should be free from toxic lead and cadmium, while designs and finishes must comply with food-safe standards.
- Bakeware: Products like casserole dishes, baking trays, and other heat-exposed ceramics require robust thermal shock resistance. These items must endure sudden changes in temperature without cracking or breaking. Non-toxic, heat-resistant glazes are essential to ensure safety during use.
- Decorative Items: While decorative ceramics are often not subject to food-grade standards, they should still comply with general safety requirements. Paints, coatings, and finishes must be free from hazardous substances like lead and harmful volatile organic compounds (VOCs) to avoid long-term health risks.
- Storage Jars and Containers: Ceramic jars and containers used for food storage must provide airtight sealing capabilities and comply with food-contact safety standards. Testing for leaching and chemical stability is critical for these items.
- Plant Pots: Although not intended for food use, plant pots must be free from harmful paints or finishes that could release toxins into the environment. For pots used indoors, materials should also meet fire resistance and durability requirements.
- Vases: Vases, especially those used with water or live plants, should be non-porous and free of harmful substances to avoid contamination of water or plant roots. This is particularly important for vases in direct contact with fresh produce or edible flowers.
- Customised Ceramics: Custom-designed ceramic products may require additional safety testing depending on the materials and processes involved. For example, unique glazing techniques or added decorations must align with safety regulations.
- Children’s Ceramics: Items designed for children, such as ceramic dishes or mugs with child-friendly designs, should comply with stricter safety guidelines to ensure they are non-toxic and free of sharp edges or small parts.
Testing and Compliance Requirements
Importers should ensure that products meet safety standards through:
- Certified Laboratories: Conduct lead, cadmium, and thermal shock tests.
- Pre-shipment Inspections: Randomly sample and test batches before shipping.
- Proper Documentation: Maintain compliance reports and certifications for each shipment.
Consequences of Non-Compliance
Failing to meet ceramic safety standards can result in:
- Legal Penalties: Heavy fines and import bans.
- Reputation Damage: Loss of trust among customers and partners.
- Financial Losses: Costs for recalls, re-testing, and disposal of non-compliant products.
How to Choose a Reliable Ceramic Supplier
To ensure compliance, importers should:
- Verify the supplier’s certifications and testing records.
- Visit the factory or request detailed reports.
- Partner with suppliers who provide customisation while adhering to global safety standards.
Tips for Importers to Stay Compliant
- Stay updated on changing regulations in target markets.
- Invest in quality assurance and third-party audits.
- Consult legal and compliance experts regularly.
Conclusion
Understanding and adhering to ceramic product safety standards is essential for importers. Compliance protects consumers, prevents legal issues, and ensures business success. Partnering with a reliable supplier like Homey Ceramic ensures that your products meet global safety standards while offering exceptional quality and design.
FAQs
What are the most common safety tests for ceramic products?
Tests for lead and cadmium content, thermal shock resistance, and chemical safety are standard.
How often should products be tested for compliance?
Products should be tested annually or with any significant change in materials or manufacturing processes.
Are decorative ceramic items subject to the same regulations as tableware?
No, but they must still meet general safety standards for paints and coatings.
What documentation should I request from my supplier?
Importers should request compliance certificates, testing reports, and material safety data sheets (MSDS) to ensure adherence to safety standards.
What happens if my products fail a safety test?
If your products fail a safety test, you may need to re-test the batch, recall products, or modify production processes to meet standards. This can incur significant costs and delays.
How can I stay informed about changing safety regulations?
Subscribe to updates from regulatory bodies, join industry associations, and work with compliance experts who can monitor and inform you about relevant changes.
Is it more expensive to ensure compliance with all safety standards?
While compliance may add to production and testing costs, it prevents costly legal issues, recalls, and reputational damage, ultimately saving money in the long run.
Can handmade ceramics comply with safety standards?
Yes, handmade ceramics can meet safety standards if they use certified materials and undergo proper testing and inspections.
Do I need to test every shipment of ceramics?
Testing every shipment isn’t always necessary if your supplier provides consistent results. However, periodic random testing is a good practice.
How can I ensure my supplier is reliable?
Verify their certifications, conduct factory audits, and request detailed compliance documentation to build trust and ensure reliability.





